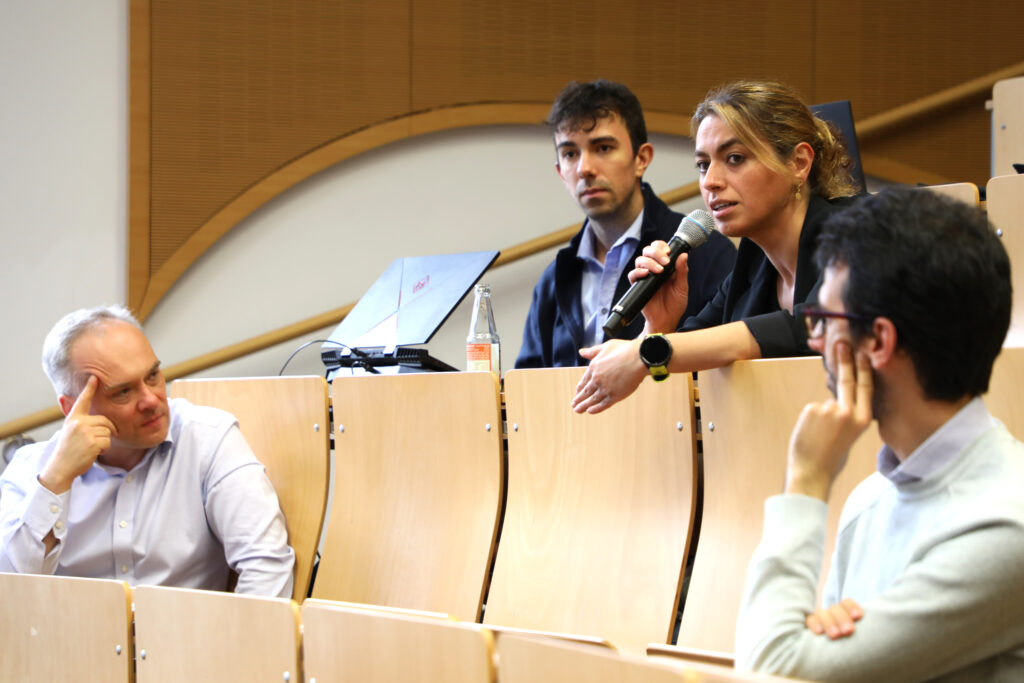
About IntelliLung
Invasive mechanical ventilation is one of the most important and life-saving therapies in the intensive care unit (ICU). In most severe cases, when mechanical ventilation alone is insufficient, extracorporeal lung support is initiated. However, mechanical ventilation is recognised as potentially harmful, because inappropriate mechanical ventilation settings in intensive care unit patients are associated with organ damage, contributing to disease burden. Studies revealed that mechanical ventilation is often not properly provided despite clear evidence and guidelines. Variables at the ventilator and extracorporeal lung support device can be set automatically using optimization functions and clinical recommendations, but the handling of experts may still deviate from those settings depending upon clinical characteristics of individual patients. Artificial intelligence can be used to learn from those deviations as well as the patient’s condition in an attempt to improve the combination of settings and accomplish lung support with reduced risk of damage. Furthermore, treatment decisions by the healthcare providers, especially regarding mechanical ventilation and extracorporeal lung support, often remain incomprehensible to the patients and their relatives, since flow of information from caregivers to patients is challenged by a number of factors, including limited time and resources, communication problems as well as patients capacity to comprehend and memorise information.